Anti-scaling innovation solution for FGD effluent evaporation
Technical background
Mechanical Vapor Recompression(MVR) is a new energy-saving evaporation technology in the evaporation system. It utilizes the secondary steam, which is pressuized and heated by a compressor and then returned to heater to serve as the evaporation heat source. It has the advantages of a compact structure, high efficiency and energy saving, stable operation, and a high degree of automation.
Rectification is a common process section in organic chemical production. The materials in the tower kettle are vaporized to generate steam. The steam rises and comes into counter-current contact with the materials sprayed at the top of the tower, relizing mass and heat transfer to achieve the purification or concentration of the materials. In conventional rectification production, a reboiler is set in the tower kettle, and live steam is used as the heat source to heat the materials. This process technology is mature, and the production is stable, but the steam consumption is relatively large, and the production cost is high.
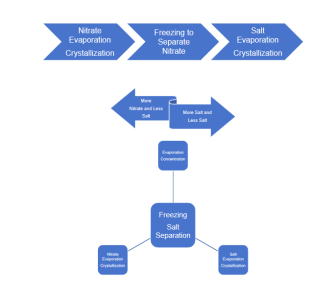
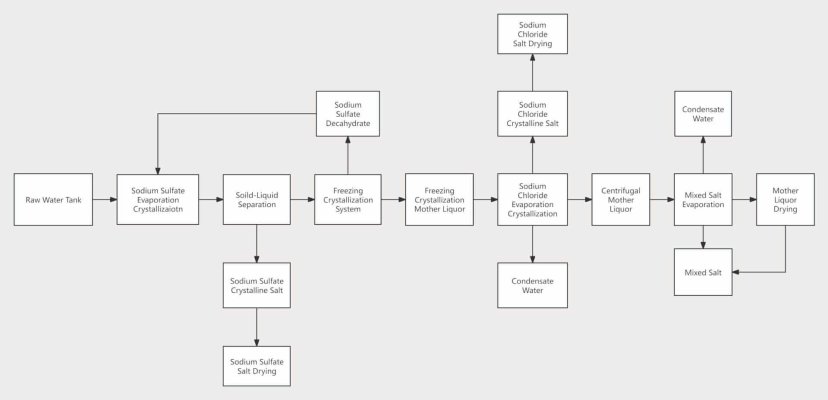
Application of MVR Evaporation in rectification system
Applying MVR technology to the rectification system can fully utilize the energy-saving and high efficiency advantages of MVR technology. This technology compresses, pressurizes and heats the light-component steam at the top of the tower through a compressor, increasing the enthalpy value. Then, it returns to the evaporator to serve as the evaporation heat source, and condenses into a liquid after releasing hear. After being collected in the condensate tank, part of the condensed light components is returned to the top of the tower for reflux, and the other part is discharged from the system.
The heavy components in the tower kettle are heated in the falling-film evaporator, and the light components are vaporized and rise. They fully contact with the light-component condensate sprayed down from the top of the tower for mass and heat transfer, thus realizing the rectifiction of the light components. The liquid in the tower kettle is concentrated due to the volatillzaiton of the light components, and is discharged from the system after reaching the required concentration.
This process makes full use of the latent heat of the secondary steam, converting low-grade steam into high-grade steam and reducing the consumption of live steam. The light-component steam is condensed in the evaporator, eliminating the need for a separate condenser at the top of the tower, reducing equipment investment. At the same time, it greatly reduces the comsumption of circulating cooling water, lowers the production cost and improves the economic benefits.
Application Prospects
Most organic substances are materials with low boiling point rise. Therefore, this technology has broad application prospects in the field of organic substance rectification. At present, the systems successfully applied by Hubei Sanfeng includ methanol rectification, DMF rectification, etc., achieving good energy-saving effects. Meanwhile, for different light-component materials, our company has developed compressors suitable for different physical properties, expanding the application prospects of this technology.
Application Case
Hubei Sanfeng successfully applied this technology in a company in Yingkou that produces methylhydrazine. An MVR compressor was used to replace live steam as the heat source. The system processing capacity is 13t/h, and the concentration of the fed methylhydrazine in the bottom product of the tower is ~47%. The system electricity consumption is about 1100kWh, and the steam saving is about 19t/h. Calculated at an electricity price of 0.5yuan/kWh and a steam price of 180 yuan/t, the operating cost can be saved by 2,870yuan per hour, and the annual operating cost can be saved by 22.96 million yuan (calculated based on an annual operation of 8000 hours). It has obvious energy-saving effects and economic benefits.
