Anti-scaling innovation solution for FGD effluent evaporation
Petrochemical Wasterwater
Wastewater in the petrochemical industry refers to the wastewater discharged by petrochemical plants. The composition of the wastewater is complex. Due to the numerous petrochemical products and the complexity of reaction processes and unit opertions, the properties of the wastewater are complex and changeable; the content of organic substances, especially hydrocarbons and their derivatives, in the wastewater is high, and it contains a variety of heavy metals. Petrochemical wastewater has many sources, diffrent composititons, and is closely related to the production process.
Introduction to Flowback Fluid.
Flowback fluid is a liquid containing solid phases that is flowback-discharged after the fracturing operation of oil and gas fields. It is generated during the exploitation process of unconventional oil and gas (or called shale oil and gas), and unconventional oil and gas occupy an increasingly important position in the current world energy strcture. However, the exploitation of shale oil and gas requires the consumption of a large amount of high-salinity wastewater. Take the United States as an example. The exploitation of shale oil and gas consumed a total of 940 billion liters of fresh water and generated 803 billion liters of wastewater between 2005 and 2014. Considering that many aress rich in shale oil and gas are located in arid and water-deficient regions, the development of the shale oil and gas industry is bringing us the dual challenges of water pollution and water resources shortage.


1212
At present, the design concept for domestic petchochemical wastewater treatment still focuses on harmless treatment. The main treatment process adopted is pretrement+evaporation desalination. Due to the complex composition of petrochemical wastewater, the commonly-used processes are introduced as follows:
(1) Air flotation and oil separation
Air flotation uses highly dispersed tiny air bubbles as carriers to adhere to suspended solid in wastewater, making them float to the water surface along with the air bubbles for separation. The objects of separation are petrochemical oil and hydrophobic fine solid suspended solids. In the treatment of petrochemical wastewater, air flotation is often set after oil separation and flocculation and has wide applications.
Petrochemical wastewater contains relatively large amount of floating oil, which will be adsorbed on the surface of activated sludge particles or biofilms, making it difficult for aerobic organisms to obtain oxygen and thus affecting their activity, bringing adverse effects on biological treatment. Generally, an oil separation tank is used for removal. The oil separation tank also serves as an inital sedimentation tank, removing settleable substances such as coarse particles, and reducing the dosage of flocculants in subsequent treatment.
(2)adsorption
Adsorption is a method that utilize the porosity of solid substances to make pollutants in wastewater adhere to their surfaces for removal. The commonly used absorbent is activated carbon, which can effectively remove the color, odor, COD, etc. of wastewater. However, the treatment cost is relatively high, and it is likely to cause secondary pollution. In the treatment of petrochemical wastewater, adsorption is often used in combination with ozone oxidation or flocculation.
(3) Membrane Separation
Membrane separation is a modern high-tech technology that uses functional membranes as separation media to achieve highly efficient separation and purification of liquids or gases. It mainly includes reverse osmosis, nanofitration, and microfiltration. It can effectively remove the color, odor of wastewater, and get rid of various ions, organic substances, and microorganisms. Compared with existing separation processes, the membrane separation processes have no phase change, operate at normal temperature, and the equipment and process are simple. The quality of the effluent water is stable and reliable, and the floor area is small. The operation is fully automated. However, it requires a large investment and has a small sewage treatment capacity.
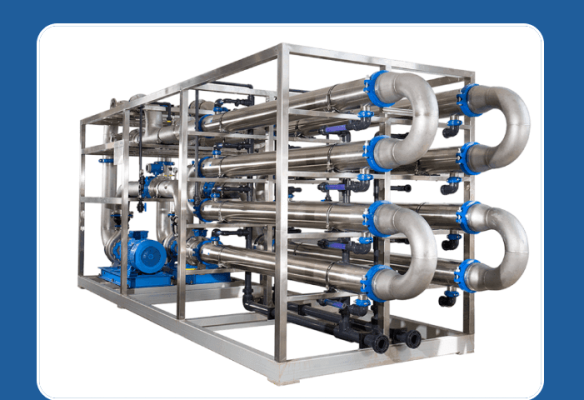

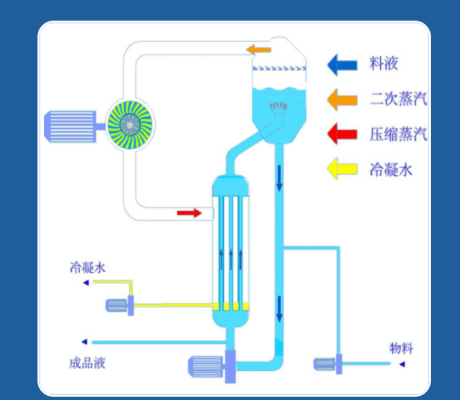
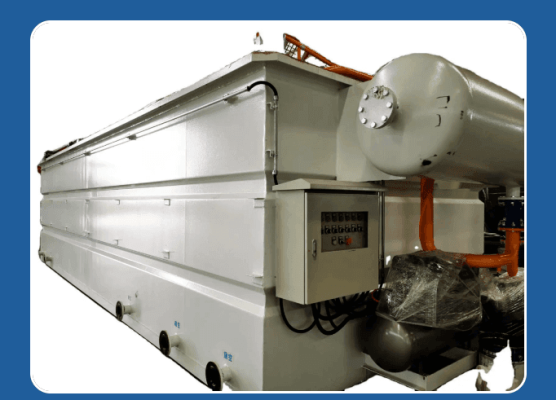
(4)evaporation and desalination
For petrochemical wastewater with high COD or the concentrated membrane water produced after membrane separation, due to its relatively high salt content and the content of other impurities (such as COD, ammonia nitrogen, etc.), it cannot be directly discharged. Therefore, evaporators, as common desalination devices, are widely used in the petrochemical wastewater treatment industry. On one hand, the quality of the condensed water generated by evaporation is relatively good. It can either be reused as reclaimed water or directly discharged. The salt generated by evaporation is packaged and then transported outside for treatment.
